School-Productive Farm with renewable energy sources in Palmira municipality
Main Article Content
Abstract
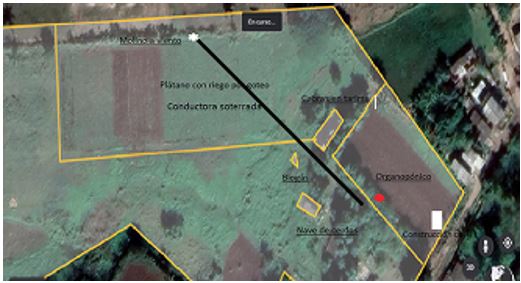
The productive school farm aims to contribute to food sovereignty in the municipality through technologies that use renewable energy sources, promoting a culture of good sustainable agroecological practices, nutritional education and efficient irrigation systems. The land has an organoponic with a mesh cover for shade and micro-sprinkler irrigation fed by photovoltaic solar pumping; a shed with a pallet for raising goats; an area of 0.5 hectares planted with bananas, with drip irrigation fed by a windmill; a shed for fattening pigs; an area for waste treatment (biogas); an area for wastewater treatment (biogas); an area for the treatment of wastewater (biogas); and an area for the treatment of wastewater (biogas); an area for waste treatment (biogas, compensation tank, sedimentation pit and fertigation tank); a civil construction of masonry and light, single-water roof, with a 17° slope that allows for the installation of photovoltaic solar panels to power the organoponic irrigation system. The irrigation systems and water sources were carefully designed, resulting in a methodology to be taught in courses. The roofed area will have a rustic classroom, without walls, with high landscaping around it; a vegetable washing and selection area; a vending machine; a safe area for cheese production; a storage area for farm implements; and a restroom. Considering the income in the productive part, the investment is recovered in three years. and an electricity generation capacity of 118.66 kWh per day. The economic evaluation has a long Investment Recovery Period (IRP), close to 15 years out of a useful life of 25 years, and a low Net Present Value (NPV) given that Resolution No. 435/2017 establishes the cost of the KWh, sold by
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
References
Carbonell Saavedra, E. (2017). Evaluación del sistema de riego por goteo en tomate (Solanum lycopersicum L.) en casas de cultivos. [Tesis de Doctorado, Universidad Universidad Central de Las Villas]. Universidad Central Marta Abreu de Las Villas, Villa Clara.
HF Altos caudales. Electrobombas centrífugas [Manual] (consultado: 12 de marzo de 2021). http://www.pedrollo.com/public/allegati/HF%20Medie%20portate_ES_60Hz.pdf
Cengel, C., y Mecánica, D. (2006). Mecánica de Fluidos fundamentos y aplicaciones. (Fuente)
Crespo, C. M. (2002). Mecánica de los fluidos. Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, Servicio de Publicaciones.
Criollo Tupiza, L. F. (2021). Diseño del sistema de riego por aspersión y sistema de drenaje de la cancha principal de la Liga Parroquial Zámbiza, cantón Quito, provincia de Pichincha [Trabajo de titulación previo a la obtención del Título de Ingeniero Civil, Universidad Central de Ecuador]. Repositorio Institucional – Universidad Central de Ecuador, Quito.
De las Heras, S. (2019). Fluidos, bombas e instalaciones hidráulicas. Universitat Politecnica de Catalunya. Iniciativa Digital Politecnica. (Fuente)
Escuela de Posgrado - Universidad Nacional Agraria La Molina (Epg-UNALM) (2009). Mecanismos para el aprovechamiento eólico: las máquinas eólicas. https:// www.monografias.com/trabajos-pdf2/mecanismos-aprovechamiento-eolico-maquinas/mecanismos-aprovechamiento-eolico-maquinas2.shtml
Gálvez Román, R. (2005). Diseño y cálculo preliminar de la torre de un aerogenerador [Tesis de pregrado, Universidad Carlos III de Madrid]. https://docplayer.es/17943741-Diseno-y-calculo-preliminar-de-la-torre-de-un-aerogenerador.html
García Marín, E. (2019). Tema 01 Energías Renovables. En: Studocu. https://www.studocu.com/es/document/universitat-de-valencia/gestion-energetica-energias-renovables/apuntes/tema-01-energias-renovables/2444836/view
Lodoño, A. (2019). Diseño de un sistema de riego en la granja Tarapacá ubicada en la ciudad de Santiago de Cali [Tesis de diploma, Universidad Autónoma de Occidente]. Universidad Autónoma de Occidente, Santiago de Cali.
Mendoza Balderrama, J. C., y Bermúdez Valdez, J. M. (2015). Diseño, implementación y evaluación de un sistema de riego por microaspersión en café (Coffea Arábica l.) en la ESPAM MFL [Tesis de pregrado, ESPAM]. ESPAM, Manabí.
Mendoza Vera, M. I., y Rodríguez Zambrano, W. (2012). Evaluación post-implementación de un sistema de riego por aspersión en el cultivo de cacao (theobroma cacao l.) en la ESPAM-MFL [Tesis de pregrado, ESPAM]. ESPAM, Manabí.
Modon, A. (2017). Teoría de mecánica de los fluidos apuntes. Universidad Nacional de Cuyo. http://ingenieria. uncuyo. edu. ar/catedras/apuntes-teoricos-de-mecanica-delos-fluidos-rev9-doc-prot. pdf.
Tarjuelo J. M. (2002). Agronomía del riego. La aplicación del agua con el riego y su evaluación. Departamento de Producción Vegetal y Tecnología Agraria. Universidad de Castilla – La Mancha. Ediciones Mundi – Prensa, Madrid, España.